
What’s Dystonia Chronic Pain and How Does It Feel?

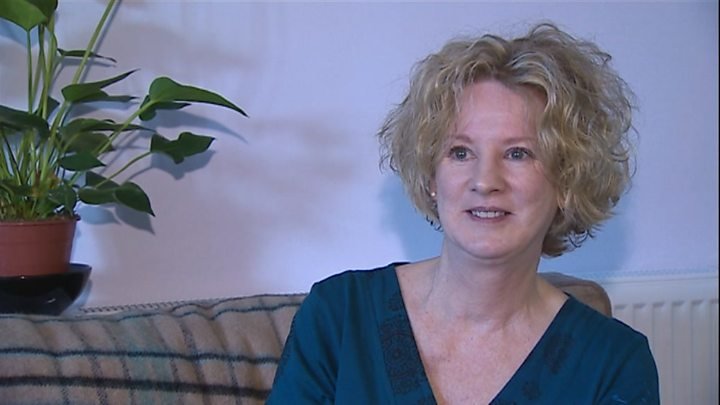
Can you imagine your muscles contract and feeling as if you didn’t have power over your body? Dystonia disease made the news after a woman from Caernarfon, Gwynedd talked about her condition in an interview, as the 56-year-old Ann Pierce-Jones said she loved to be outdoors and enjoyed interacting with other people until she found out about Dystonia. Today, she lives her life with muscle spasms that are uncontrollable, tremors in her neck that result in chronic pain with a condition described as life-changing.
Pierce-Jones is only one of the 5,000 people to suffer from this movement disorder in Wales

Ann Pierce-Jones On The Right Was One of the Victims of Dystonia
There are 500,000 people affected by Dystonia in North America while an estimated number of over 1 million are affected all over the world. Others talked about the disorder that the pain increased in months to the point of barely functioning on a daily basis with the feeling of having a power drill in the base of the skull that radiates down the neck.
What is Dystonia?
If anybody asked about essential tremors or Parkinson’s disease, they would probably have an image or impression of the disorder. Dystonia, unlike the other muscle disorders, is a condition that not many people have heard of. This medical condition is actually the third most common neurological movement disorder.
Dystonia is a disorder in the movement of muscles that are contracting uncontrollably. The abnormal posture or repetitive movement is due to the contraction and the twisting of the muscles that are involuntary. The effects of this condition vary from one muscle, a group of muscles, or the whole body.It affects 1% of the population and it is more prone to women than men.
To better explain the disorder, think about Dystonia in terms of the muscle parts.
Normally, when a muscle contracts, the opposite muscle relaxes. For instance, when you flex your biceps, your triceps coordinate with the movement by relaxing. But in the case of Dystonia, the opposing muscles move involuntarily in a simultaneous manner that results in pain, abnormal posture, and movements that awkward.
What are the symptoms?
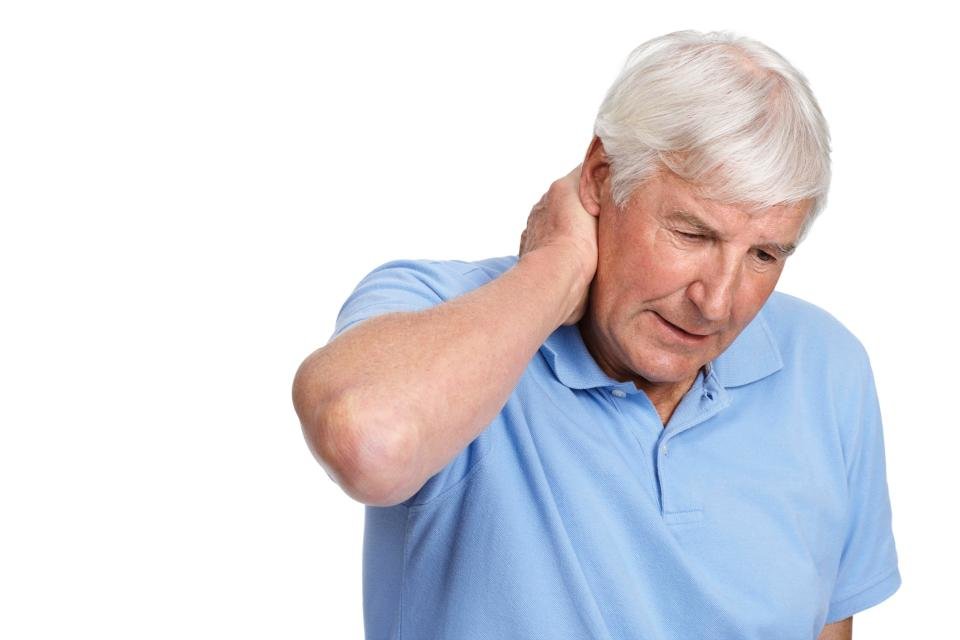
Symptoms of Dystonia Explained
The symptoms of the disorder vary from mild to severe and can affect the different body parts. It progresses through the different stages. The early symptoms to watch for are the cramping of the foot, blinking uncontrollably, dragging a leg, pulling the neck involuntarily, and difficulty in speaking.People like Pierce-Jones suffering from this are often heard complaining about the exhaustion and pain due to constant contractions of the muscles. Fatigue and stress should also be avoided since it fuels and worsens the condition.
If the symptoms of the disorder appear in childhood, they manifest initially in the hand or foot but progress rapidly to the rest of the body. However, the progress tends to slow down after adolescence. In early adulthood, it usually appears in the upper body part with slow progression of the symptoms. They remain focal and segmental that affect either a part of the body or two or multiple body parts that are adjacent.
The forms of Dystonia

The Different Forms of Dystonia Infographic
Basically, the forms of the disorder are based on the affected regions of the body.
- Cervical Dystonia– the muscles of the neck that controls the head’s position are affected. This causes the head to turn to the side, backward, or forward.
- Blepharospasm– involves the involuntary blinking of the eyes. Usually, both of the eyes are affected.
- Cranio-Facial Dystonias– a form of focal dystonia that affects the head, face, and the neck.
- Task-specific Dystonia- this is a type of the disorder when undertaking an activity that is repetitive.
Other types of Dystonia are generalized dystonia, multifocal dystonia, segmental dystonia, and hemidystonia.
The Leading Causes of this Chronic Pain
A lot of the recorded cases of the disorder do not have a specific cause but seems to be related to a certain problem in the basal ganglia. Basal Ganglia is the area of the brain that is responsible for the contraction of the muscle. The problem is linked to the communication of the nerve cells.
This chronic pain has no effect on the cognition of a person, it also does not cause to shorten life but it certainly affects the quality of life. There is no cure available as of the moment but treatments are offered to minimize the symptoms.
More in Medical Conditions
-
Is It Safe to Travel to Paris? Essential Tips for Tourists
When considering a trip to Paris, one of the first questions that often arises is, “Is it safe to travel to...
June 20, 2024 -
Hematoma vs Bruise: What Is the Difference?
When it comes to injuries, hematoma vs bruise are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different medical conditions. Understanding the...
June 12, 2024 -
What Is Unipolar Depression? Here’s What You Need to Know Right Now
Depression casts a long shadow over many lives, with symptoms that affect everything from our energy levels to our ability to...
June 7, 2024 -
A Comprehensive Guide on How to Heal Anxious Attachment Style
If you often find yourself seeking constant reassurance from your partner or requiring endless validation to feel secure, you may be...
June 1, 2024 -
Why Is My Skin Peeling on My Face After Skincare? Here’s What You Need to Know
Experiencing skin peeling on your face after implementing a skincare routine can be perplexing and frustrating. This phenomenon, where the skin...
May 23, 2024 -
What Is a Mental Edge, and How Do You Get It?
Have you ever wondered why some individuals seem unshakably confident under intense pressure, finding a way to excel when it matters...
May 15, 2024 -
When to Worry About Varicose Veins? Here’s What You Need to Know
Varicose veins are a common issue, affecting about 20% of adults. They’re usually seen as unsightly blemishes on the legs but...
May 12, 2024 -
Why Is Discipline Important: The Ultimate Guide to the Importance of Discipline
Discipline is undoubtedly one of life’s most crucial character traits. It shapes how we approach tasks, manage our time, and...
May 3, 2024 -
Have I Fallen Out of Love or Am I Depressed? Everything You Need to Know
Have I fallen out of love or am I depressed? You’re not alone in this query. In the diversity of human...
April 26, 2024













You must be logged in to post a comment Login