
Soluble Vs. Insoluble Fiber: Is One Better Than the Other?

Fiber is a carbohydrate that can be found in plant foods that plays a crucial role in a healthy diet. Although, if you’re looking for something that can fuel your body, this is not it. It’s hard for your small intestines to digest fiber unlike other kinds of carbs. With its structure, it’s hard to break it down to use as energy for your body. However, that doesn’t mean that it isn’t good for your nutrition.
There are actually two kinds of fiber, in case you didn’t know. Soluble fiber and insoluble fiber do different things but both are valuable to your body. Here’s how:

Fallon Michael / Pexels
Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber can be dissolved in water. It slows down your digestion by absorbing water and swelling up into a gel-like substance in your stomach. In this form, it will be broken down by bacteria in the large intestine and eventually help provide a few calories.
One of the main benefits of soluble fiber is that it can slow down the absorption of certain substances that can have harmful effects on your health if you have high volumes of it inside your body. For instance, it can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down carbohydrates that enter the bloodstream.
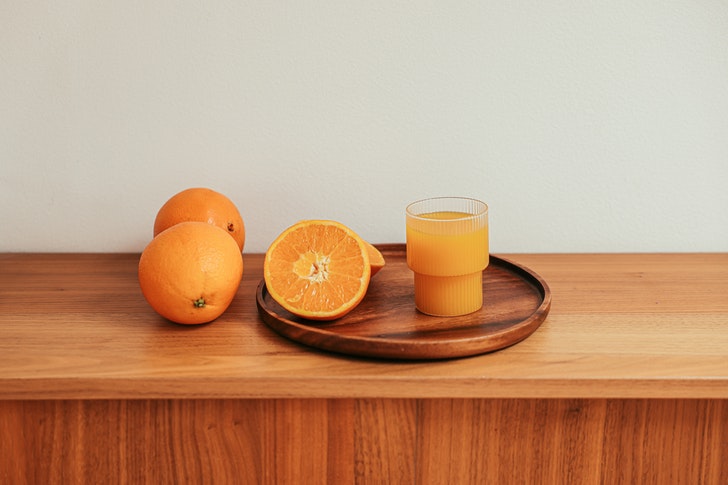
When you drink orange juice, it will be metabolized quickly and will, therefore, increase your blood sugar level faster. On the other hand, if you consume an orange fruit, the sugar uptake will only be gradual due to the soluble fiber in the citrus.
Soluble fiber can also lessen the risk of heart disease by regulating the absorption of dietary fat and help in lowering bad cholesterol.
It is mainly present in plant foods like nuts, barley, oats, beans, lentils, peas, chia seeds, citrus fruits, and berries. It is also found in some veggies like carrots, winter squash, artichokes, and broccoli.

Cup of Couple / Pexels
Insoluble Fiber
As the name suggests, insoluble fiber can’t be dissolved in water. Aside from that fact, it’s also the opposite of soluble fiber in terms of its function. While soluble fiber slows the digestion, insoluble fiber helps move digestion and adds bulk to your stool. It’s the kind of fiber you’re probably more familiar with.
The insoluble fiber in plant foods like whole grains, nuts, beans, and some veggies like cauliflower, green beans, and potatoes help prevent and treat constipation as well as hemorrhoids. It can also aid in treating irregular bowel movements.
It also helps in managing your weight as the added volume of eating insoluble fiber-rich food can make you feel fuller after your meal. This is also something that soluble fiber can do.

hermaion / Pexels
Even though they have different roles, nothing is better than the other. On the contrary, we need a balance of both in our diets. However, you shouldn’t overthink it too much. Consuming too much of something good may turn out bad, and it’s the same for fibers.
Overloading fiber in your diet can make you experience stomach cramps, bloating, and even gas. Taking fiber supplements or fiber-fortified food to make up for a low-fiber diet can also cause the same things.
More in Weight Loss and Diet
-
Is It Safe to Travel to Paris? Essential Tips for Tourists
When considering a trip to Paris, one of the first questions that often arises is, “Is it safe to travel to...
June 20, 2024 -
Hematoma vs Bruise: What Is the Difference?
When it comes to injuries, hematoma vs bruise are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different medical conditions. Understanding the...
June 12, 2024 -
What Is Unipolar Depression? Here’s What You Need to Know Right Now
Depression casts a long shadow over many lives, with symptoms that affect everything from our energy levels to our ability to...
June 7, 2024 -
A Comprehensive Guide on How to Heal Anxious Attachment Style
If you often find yourself seeking constant reassurance from your partner or requiring endless validation to feel secure, you may be...
June 1, 2024 -
Why Is My Skin Peeling on My Face After Skincare? Here’s What You Need to Know
Experiencing skin peeling on your face after implementing a skincare routine can be perplexing and frustrating. This phenomenon, where the skin...
May 23, 2024 -
What Is a Mental Edge, and How Do You Get It?
Have you ever wondered why some individuals seem unshakably confident under intense pressure, finding a way to excel when it matters...
May 15, 2024 -
When to Worry About Varicose Veins? Here’s What You Need to Know
Varicose veins are a common issue, affecting about 20% of adults. They’re usually seen as unsightly blemishes on the legs but...
May 12, 2024 -
Why Is Discipline Important: The Ultimate Guide to the Importance of Discipline
Discipline is undoubtedly one of life’s most crucial character traits. It shapes how we approach tasks, manage our time, and...
May 3, 2024 -
Have I Fallen Out of Love or Am I Depressed? Everything You Need to Know
Have I fallen out of love or am I depressed? You’re not alone in this query. In the diversity of human...
April 26, 2024













You must be logged in to post a comment Login